Data: Archive
Creating a sustainable business practice.
#Documentation #Digitizing #Records
A practical strategy for the modern brand.
Future-proofing.
Physical data records can be a risk to your business security, reliability & performance. With the ProjektID data archive service, you'll receive a progressive ideology of managing data, while benefiting from the digitisation of all of your client records. Capturing & storing every piece of client data can assist your brand in dynamically evolving its ecosystem.
Consent.
In a world filled with privacy and personal rights, being honest with clients is classic.
Reclaim.
Never lose out on the potential uses of every single piece of data that you collect. It may just develop your business a solution.
Tactical.
Planning & utilising data can be a tactical advantage in streamlining services, or even bolstering particular products stocks.
Hard copies.
There will always be initial manual entries when collecting customer data. This is typically done through hard copies, such as surveys & contracts. Once this data is in the system, it exists forever.
Lightening quick.
Having easy & quick access to data will enable your business to examine key upgrades to your operations, quickly.
Evolution is progression.
Working outside your comfort zone can be annoying. Let alone even comprehend why physical records should be digitised. One thing is for sure, brands need to evolve in order to progress beyond competitors.
Custom solution.
If the price seems too good to be true then it most likely is not a custom service. ProjektID provides quality bespoke solutions.
Brand asset.
Your business is only acquiring a solution to solve a problem you are also gaining the upper hand to surpass performance past your competitors.
Step-by-step.
Throughout a ProjektID service, you will be kept in the loop through the entire design and development of your branded solution.
Critical thinking.
Businesses run on data. You may not know it, or even implement capturing this vital commodity. But, this is the fuel for survival. ProjektID can assist your business with capturing, organising and preparing your existing physical records ready to be imprinted onto a digital system. Utilising the premium Dropbox file storage & sharing system, you'll be able to easily and quickly backup important digitised documents while being able to share these with employees and clients.

Problem-solving principles.
At ProjektID, we embrace 5 principles that allow us to provide a bespoke solution that solves your business’s problems. There is no cut and paste models in our services, only effective planning, developing, designing and implementation of work that provides your brand with meaningful value.
-
ProjektID can develop a strategy that works in tandem with your brand and the products/services that you provide to your customers/clients. First, we will engage in an intuitive workshop, which will allow both parties to deduce essential information about your business, including:
• Qualitative and quantitative industry data.
• Brand story and core unique characteristics.
• Goals and challenges.
• Strengths and weaknesses.
• Opportunities and threats.
-
Interacting with an existing audience is great for generating input. This can assist in focusing on perceptions of the products/services and the strategic B2B positioning too. Typical questions include:
• What do they like about your products/services?
• What benefits do they receive?
• Were they a customer/client of a previous business?
• Are there any recommendations for improvement?
-
The voice and personality of your brand are unique. Configuring these to flow throughout your whole business will avoid confusion. Hosting productive cross-functional meetings is an optimal method for integrating the brand positioning and mission statement together with:
• Strategies.
• Mock-ups.
• Copywriting.
• Online and offline operations.
• A guidelines dossier.
• An identity manual.
-
Your business’s target market share the same values, behaviours and personality traits as your brand. Now is the time to raise a community. A strong brand needs strong business assets, such as:
• Branded website development and designing.
• Powerful video marketing.
• Copywriting, social media and digital marketing.
• Graphic design assets.
-
When launching the business solution, developed and designed by ProjektID, you have a unique opportunity to decide how you wish to market your brand in the industry. Managing and maintaining the business assets is key for short-term and long-term growth. If the business assets are ignored then there is a potential for a collapse in performance.
Keeping an eye on the business’s assets metrics and feedback can control the execution of the launch and make adjustments if needed to achieve your brand’s objectives for the end-goal to stick the landing.
“It pays to provide record security to your clients, it also pays to reclaim niched data for your business”
Rough order Of magnitude.
A Rough Order of Magnitude Estimate (ROM estimate) is a ‘ballpark’ estimation of a project's scale and cost. ROM estimates are not representative of every project budget, rather a comprehension of the scope-to-budget ratio. Every project is unique and requires a particular range of solutions to assist a business in solving problems. Please do contact us to organise an initial meeting to discuss your project (scope, budget & timeline). Keep in mind that the price reflects the content, skill and technical complexity of this solution and in turn can generate better value for your business.
Medium Business
Approximate Duration: 3 Months
Small Business
Approximate Duration: 2 Months
Personal Business
Approximate Duration: 1 Month
€3,293.42
€1,791.51
€336.75
-
Business records involve information pertaining to a client in a wide manner of aspects. These include correspondence records, accounting records, legal records, personnel records, progress records and miscellaneous records.
-
Essential records, also known as vital records or mission-critical records, are the records necessary for ever day business performance, resuming or continuing operations. Reducing non-essential records assists in space recovery and a focus on business-valued information over clutter.
-
A record is any document (paper or electronic) created or received by offices or employees that allows them to conduct business. This definition includes, but is not limited to: correspondence, forms, and reports. Record handling is the process of maintaining control of documentation. Clear and concise procedures can maintain the efficiency of use and effectiveness in record handling between employees and clients.
-
A record is any document (paper or electronic) created or received by offices or employees that allows them to conduct business. This definition includes, but is not limited to: correspondence, forms, and reports. Record handling is the process of maintaining control of documentation. Clear and concise procedures can maintain the efficiency of use and effectiveness in record handling between employees and clients.
-
A record is any document (paper or electronic) created or received by offices or employees that allows them to conduct business. This definition includes, but is not limited to: correspondence, forms, and reports. Record handling is the process of maintaining control of documentation. Clear and concise procedures can maintain the efficiency of use and effectiveness in record handling between employees and clients. Advanced record handling will incur additional charges.
-
Digitisation is the process of converting information from a physical format into a digital one. When this process is leveraged to improve business processes, it is called digitalisation. The results of this process are called digital transforma- tion. Prioritization uses defined rules to determine which data source takes priority over other data sources when configura- tion data sets. Prioritization of data, uses rules to create an ordered list of data sources.
-
A data collection strategy involves gathering quantitative or qualitative data. Quantitative data is data expressing a certain quantity, amount or range. Usually, there are measurement units associated with the data. Qualitative data, also known as categorical data, is defined as the data that approximates and characterizes. Types of quantitative and qualitative data collection methods include: Surveys, Online Tracking, Online Marketing Analytics and Social Media Monitoring.
-
Terms Of Service (TOS) and Privacy Policies agreements are both, as the names imply, legally binding contracts. The main difference between these two types of agreements is this: A Privacy Policy agreement exists to protect your clients. A TOS agreement exists to protect you, the business (company).
-
The General Data Protection Regulation, or GDPR, is a European privacy law that went into effect May 25, 2018. The GDPR regulates how individuals and organizations may collect, use, and retain personal data, which affects business operation and workflow. This focuses on: #1 Lawfulness, fairness & transparency, #2 Purpose limitation, #3 Data minimisation, #4 Accuracy, #5 Storage limitation, #6 Integrity & confidentiality (security), and #7 Accountability.
-
Throughout the project, receive ongoing & regular technical consultations. Gain an in-depth understanding of the project & phases, business asset(s), and strategic & technical guidance that assists your brand.
-
Once a project is complete and 100% of the budget is fullfiled, a certificate of ownership will be provided.
Service roadmap.
Comprehending the complete development processes is key in maximising the performance of a project’s success. ProjektID works in tandem with clients in order to maintain operational control to every single detail.
-
Approximate Duration: 3 Days
Approximate Duration: 3 Days
Approximate Duration: 3 Days
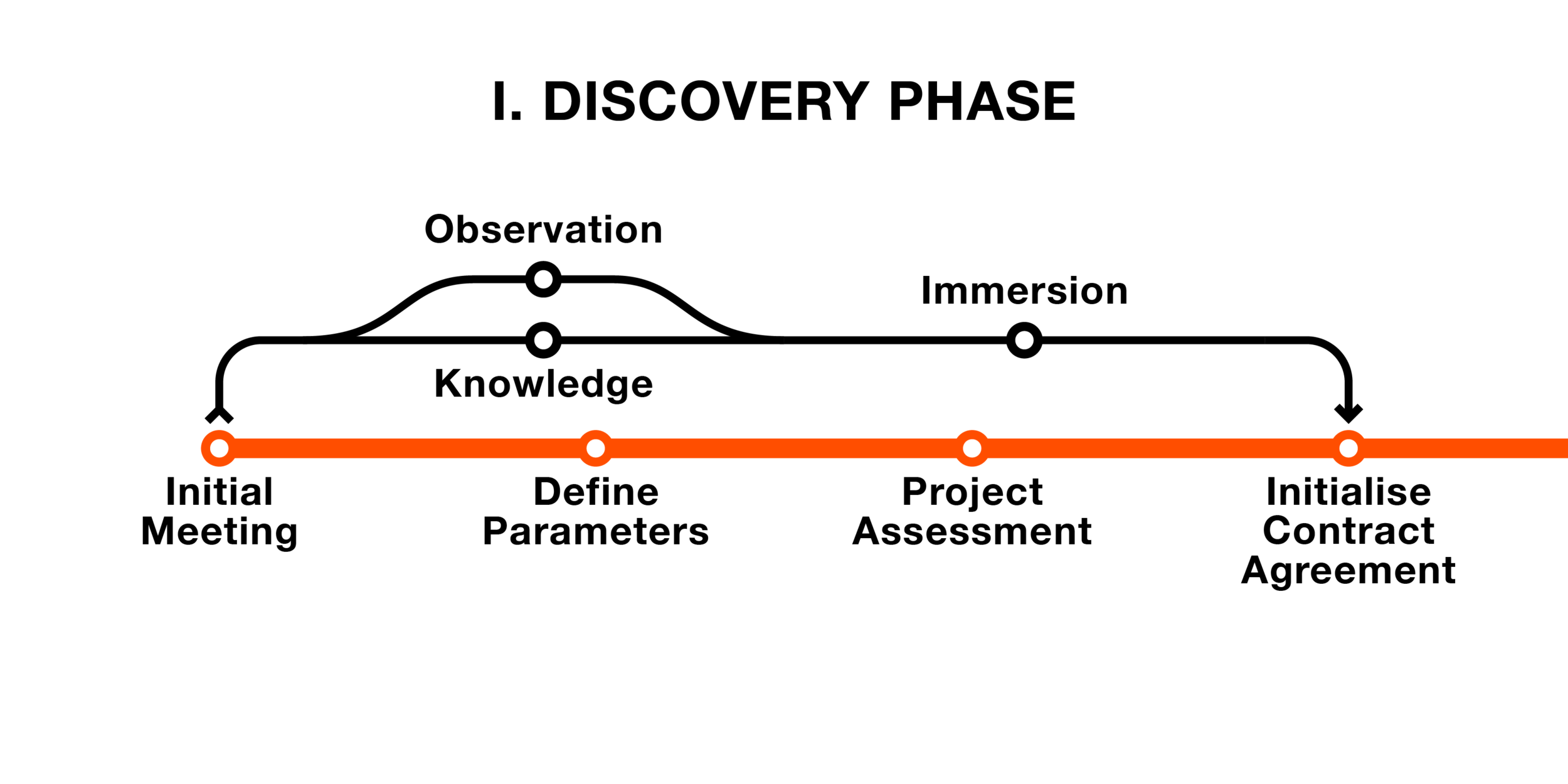
Discovery Phase
In the Discovery phase, ProjektID will need to initially define the scope of the project. This is done through an initial meeting with the client. Then the project parameters can be defined along with an assessment of the project. Once all of this is complete, the project ‘Authorisation To Proceed’ (ATP) Contract will need to be agreed to and the project will commence.
-
Approximate Duration: 25 Days
Approximate Duration: 17 Days
Approximate Duration: 8 Days
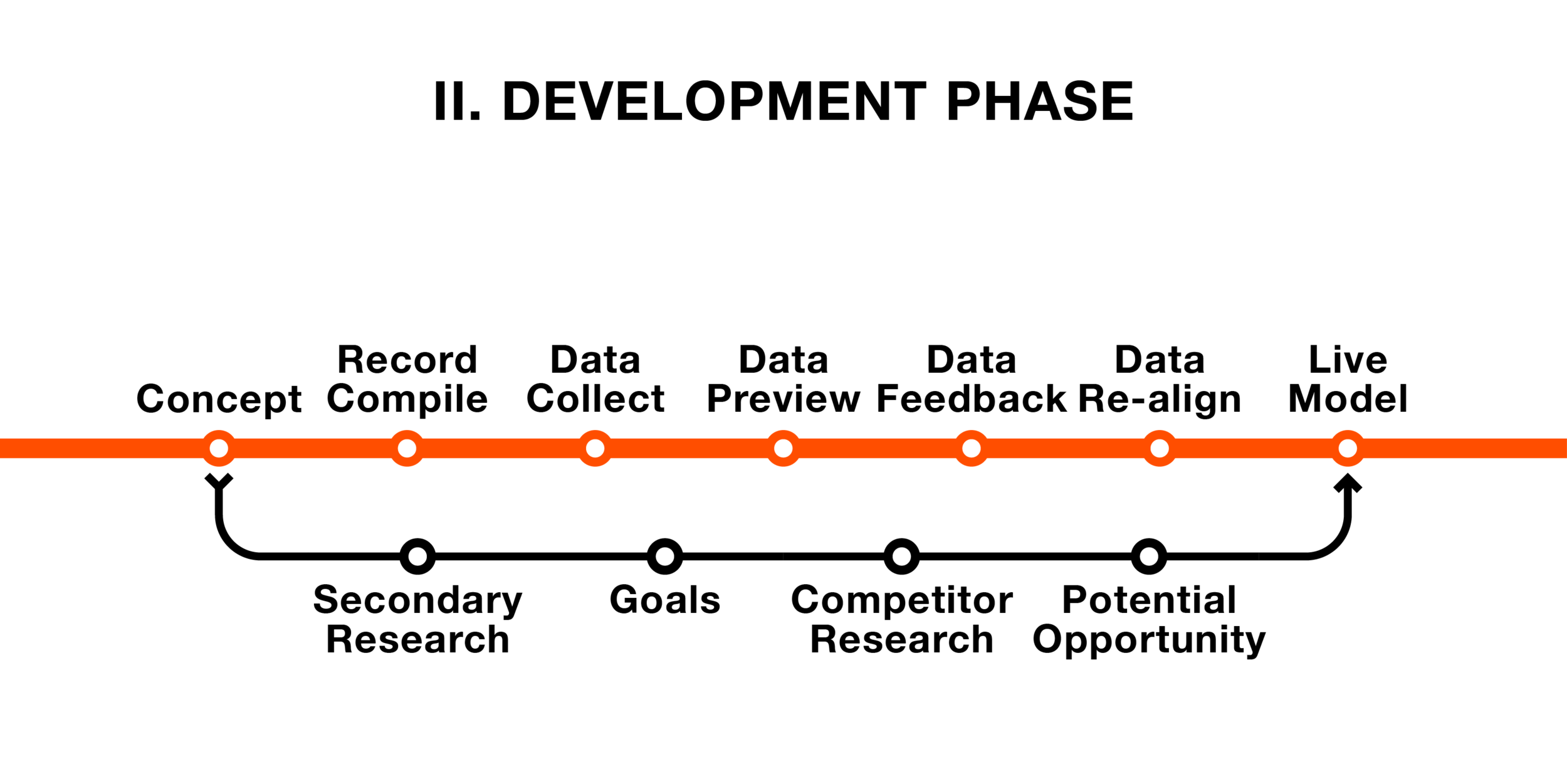
Development Phase
In the Development phase, the solution will undergo creation. A demonstration live model will then be created. All of these will be displayed to the client for feedback and agreement.
-
Approximate Duration: 14 Days
Approximate Duration: 9 Days
Approximate Duration: 4 Days
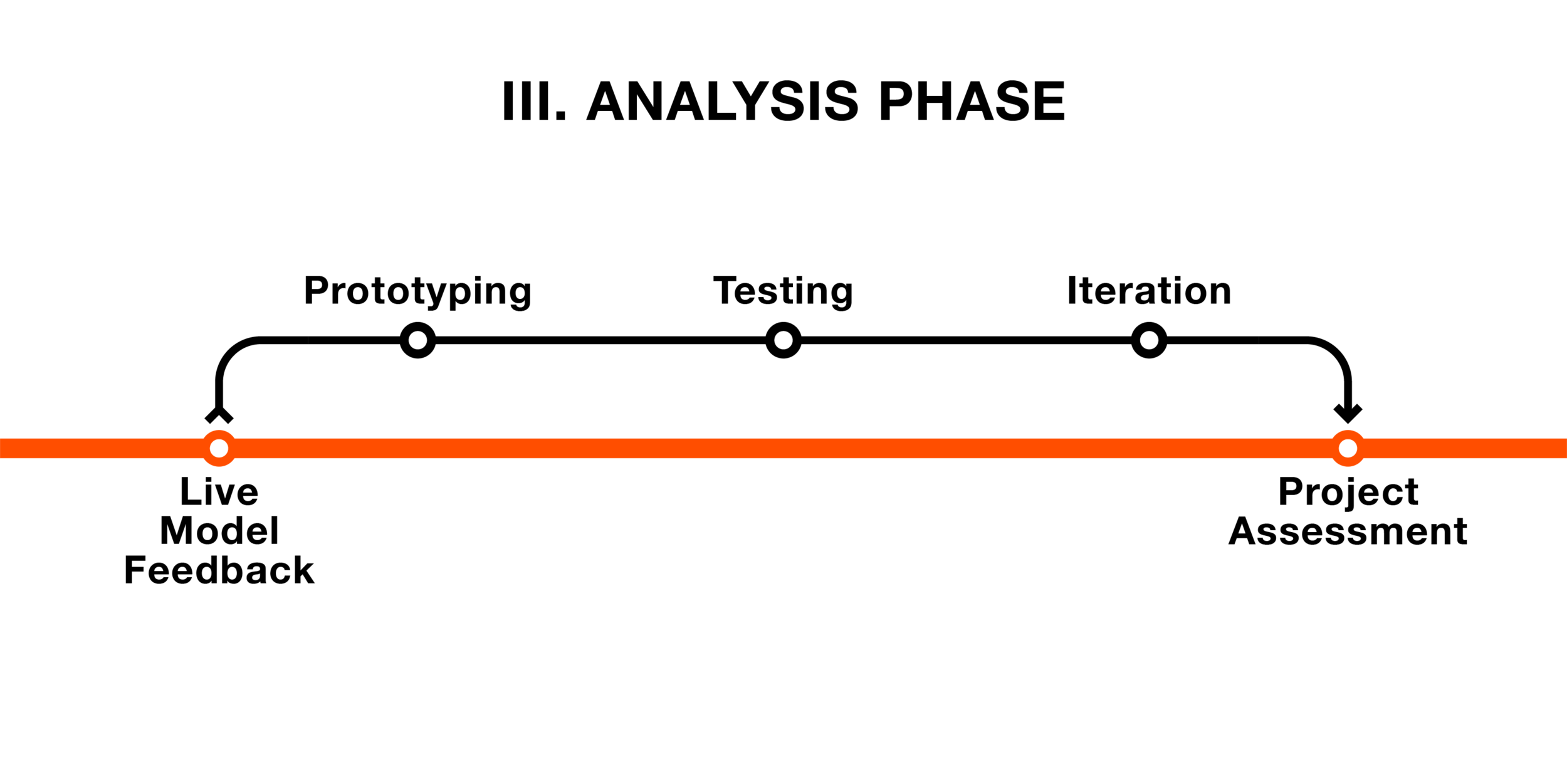
Analysis Phase
The Analysis phase focuses on gaining real feedback from asset testers. Live model testing will enable ProjektID and the client to better define the business asset and to assess the project thus far.
-
Approximate Duration: 26 Days
Approximate Duration: 17 Days
Approximate Duration: 9 Days
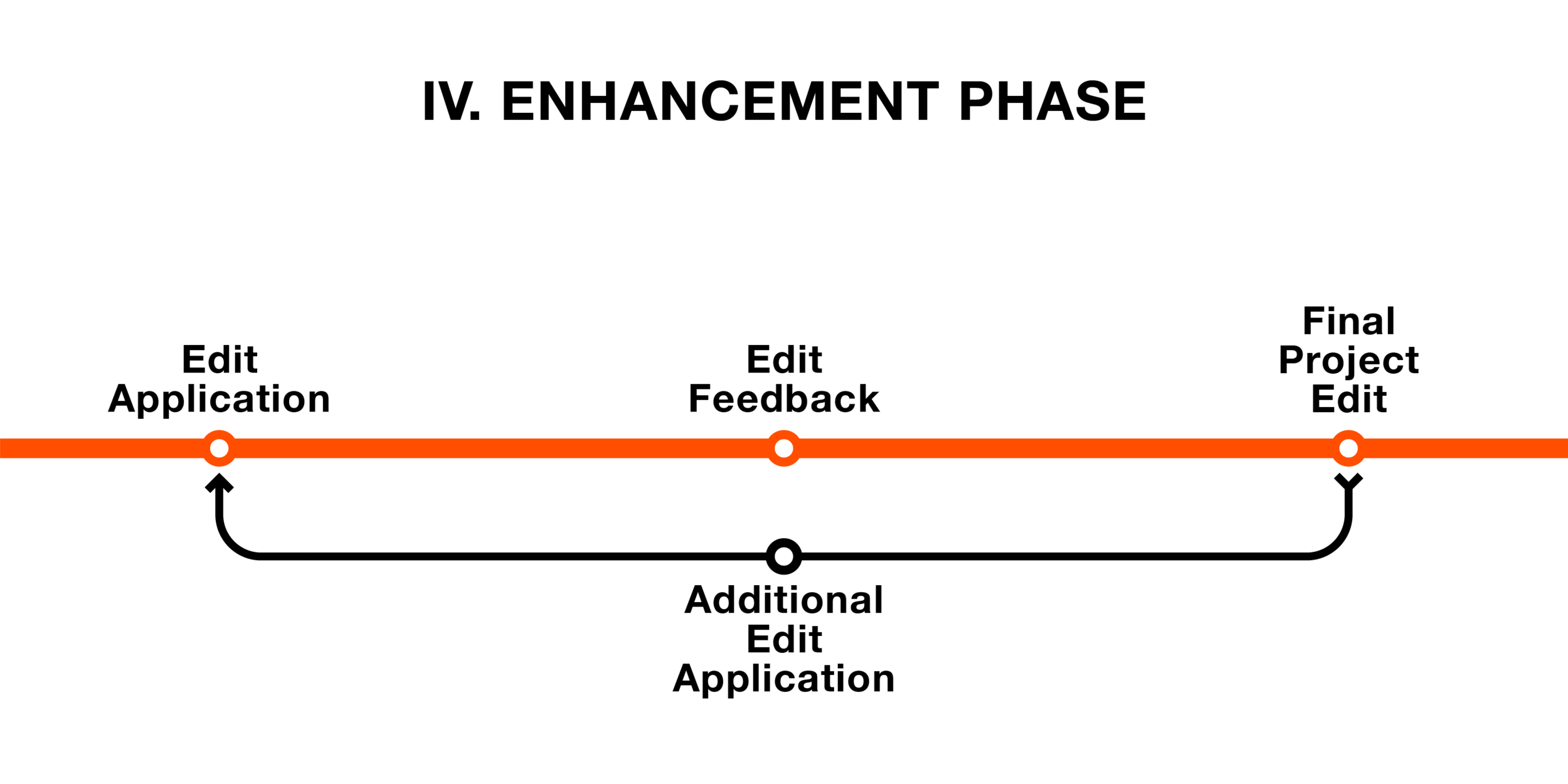
Enhancement Phase
The Enhancement phase will enable ProjektID to implement any small and big alterations to the asset from the feedback in the Analysis phase. If the final project edits still do not fulfil the project scope then additional edit applications will be enacted until complete.
-
Approximate Duration: 3 Days
Approximate Duration: 3 Days
Approximate Duration: 3 Days
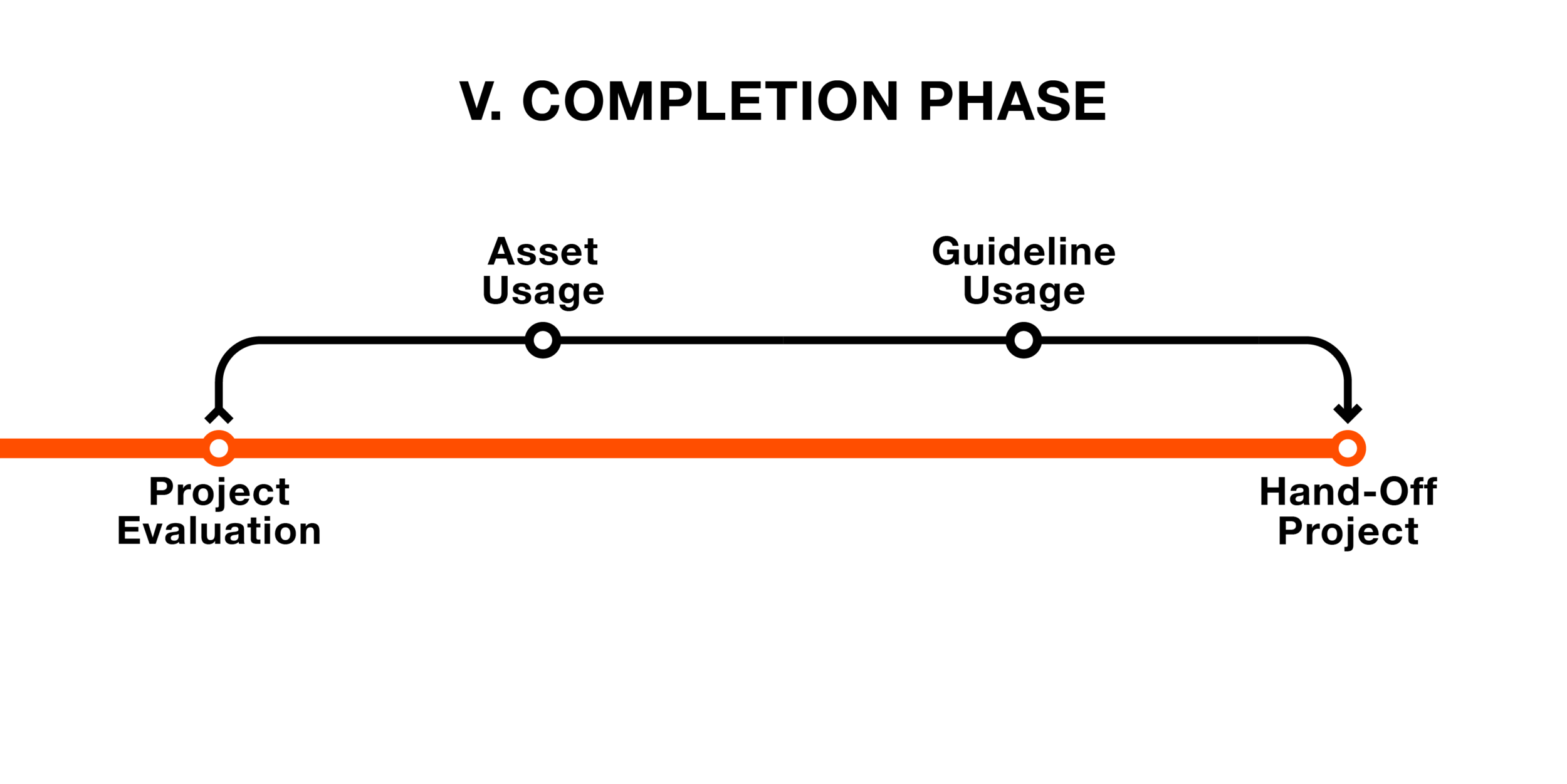
Completion Phase
In the Completion phase, both ProjektID and the client will evaluate the project together. Once the project has fulfilled the objectives in the whole project scope, the project will be handed off to the client.
Project glossary.
A glossary is an alphabetical list of terms in a particular domain of knowledge with the definitions for those terms.
Budget
The amount of money that a person, group, or organization has available to spend on a ‘project’. A budget defines the maximum and minimum values allocated to generate a particular outcome.
Project
A piece of planned work or activity that is completed over a period of time and intended to achieve a particular aim.
Project Complexity
The condition of lacking simplicity of a problem. A set of problems that consists of many parts with a multitude of possible interrelations, being of high consequence in the decision-making process that brings about the final result.
Project Scale
A determining factor from ‘Project Scope’, is most simply defined as the degree and extent to which project management practices are formally applied. Taking a "one size fits all" approach is unwise and impractical.
Project Scope
Features and functions of the scope of work needed to complete a project. Scope involves gathering information required to initialise a project, and the features the project would have that the client requires.
Project TimeLine (Duration)
A period of seconds, minutes, days, hours, weeks, months, or years, in which something may happen or in which something may occur.
Quality Control (QC)
This is a process through which a business seeks to ensure that product quality is maintained or improved. Quality control requires creating an environment in which a project strives for perfection.
Roadmap
Provides a strategic overview of the major elements of a project. This usually includes objectives, milestones, deliverables, resources, and a planned timeline.
Service Element Deliverable (SED)
A sub-division of Project Scope, a Service Element Deliverable is an action that is performed within a specific aspect of a project in order to serve a purpose. Multiple actions together (SEDs) compose the scope of work.
Stage (Phase)
A collection of activities within a project. Each project phase is goal-oriented and ends at a milestone. Reaching these milestones means the project progresses. Each phase can be divided into sub-phases.
Stage (Plan)
These include things to do, short-term and long-term objectives, and other actions that affect project completion.
Stage (Progress)
These include milestones, goals achieved, finished tasks and validated items that contribute to project completion.
Variable
A variable is any factor, trait, or condition that can exist in differing amounts or types. A project usually has three kinds of variables: independent, dependent, and controlled.
Variable (Control)
A control variable, or constant, in project development is an element which is constant and unchanged throughout the course of the project. The control variables themselves are not altered throughout any project scale.
Variable (Dependent)
The variable is measured during project development and is 'dependent' on the independent variable. In a project, the effect on the dependent variable is caused by altering the independent variable.
Variable (Independent)
The variable being manipulated during project development and is assumed to have a direct effect on the dependent variable. This determines the cause and effect of a project.
Project scale.
‘Project Scale’ is a determining factor from ‘Project Scope’ and ‘Project Complexity’, most simply defined as the degree and extent to which project management practices are formally applied. It is unwise and impractical to take a ‘one size fits all’ approach to each project, as there will be unique problems to solve along with varying scales, scopes and complexities to assess.
Project Scale = Project Scope X Project Complexity
Project variable.
A variable is any factor, trait, or condition that can exist in differing amounts or types. A project usually has three kinds of variables: independent, dependent, and controlled.
Control Variable
The control variable, or constant, in project development is an element that is constant and unchanged throughout the course of the project. The control variables themselves are not altered throughout any project scale.
Quality Control
Independent Variable
The dependent variable is what gets measured during project development, and is 'dependent' on the independent variable. In a project, the effect on the dependent variable is caused by altering the independent variable.
Timeline
Dependent Variable
The independent variable is what gets manipulated during project development, and is assumed to have a direct effect on the dependent variable. This determines the cause and effect of a project.
Budget
Our projects.
Developing a specific strategy for a business in a unique situation, within both the digital and physical world, has allowed us to vary our mindset to solve specific problems. Take a peek at some projects that we have been excited to work on.






2021